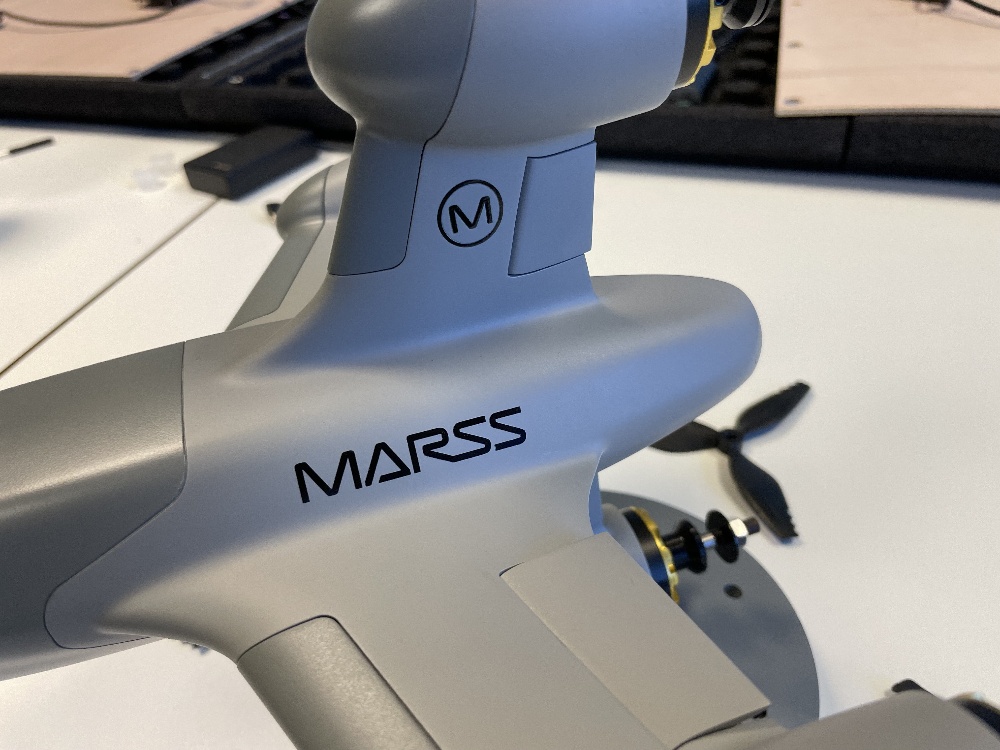
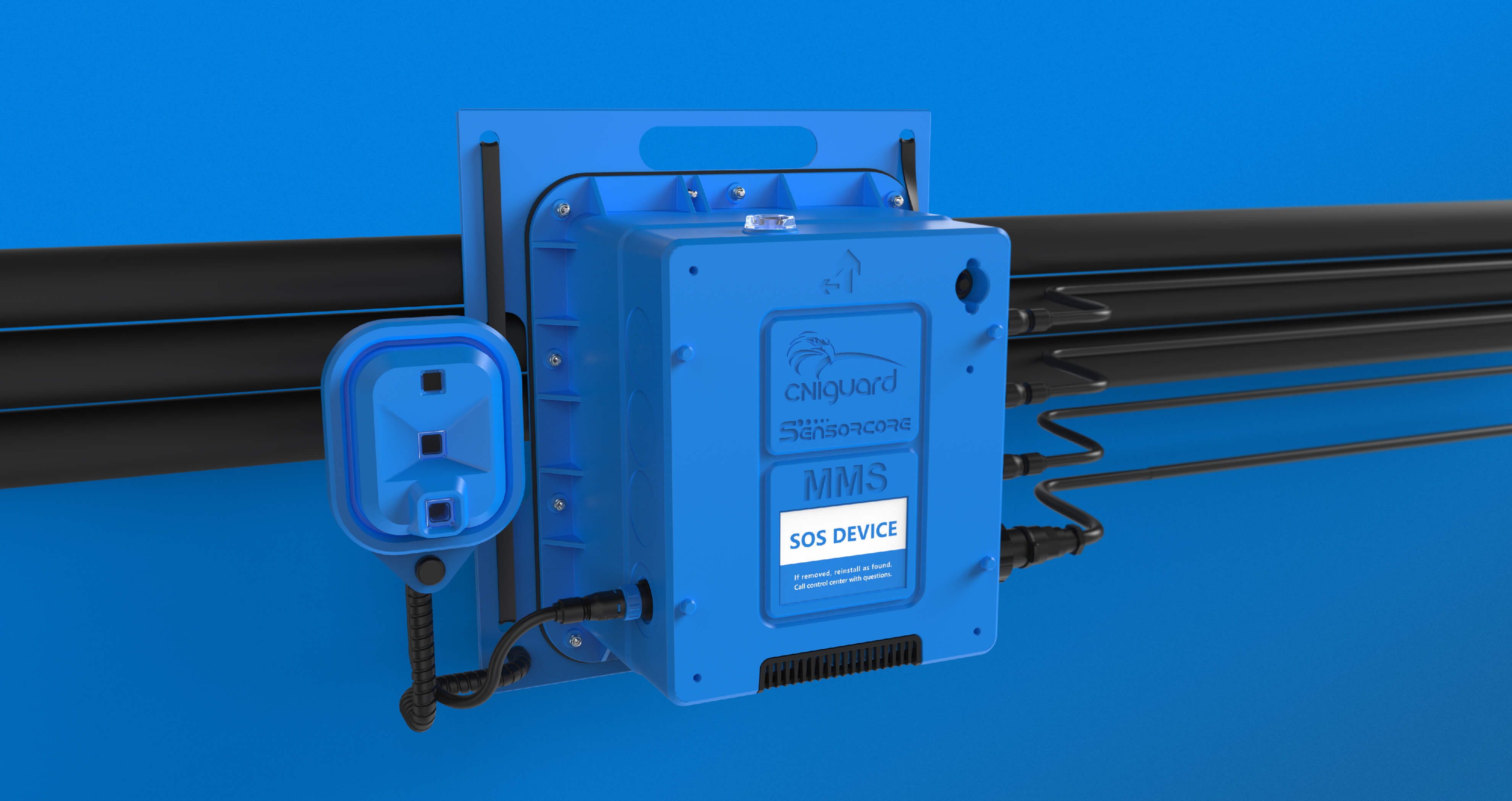
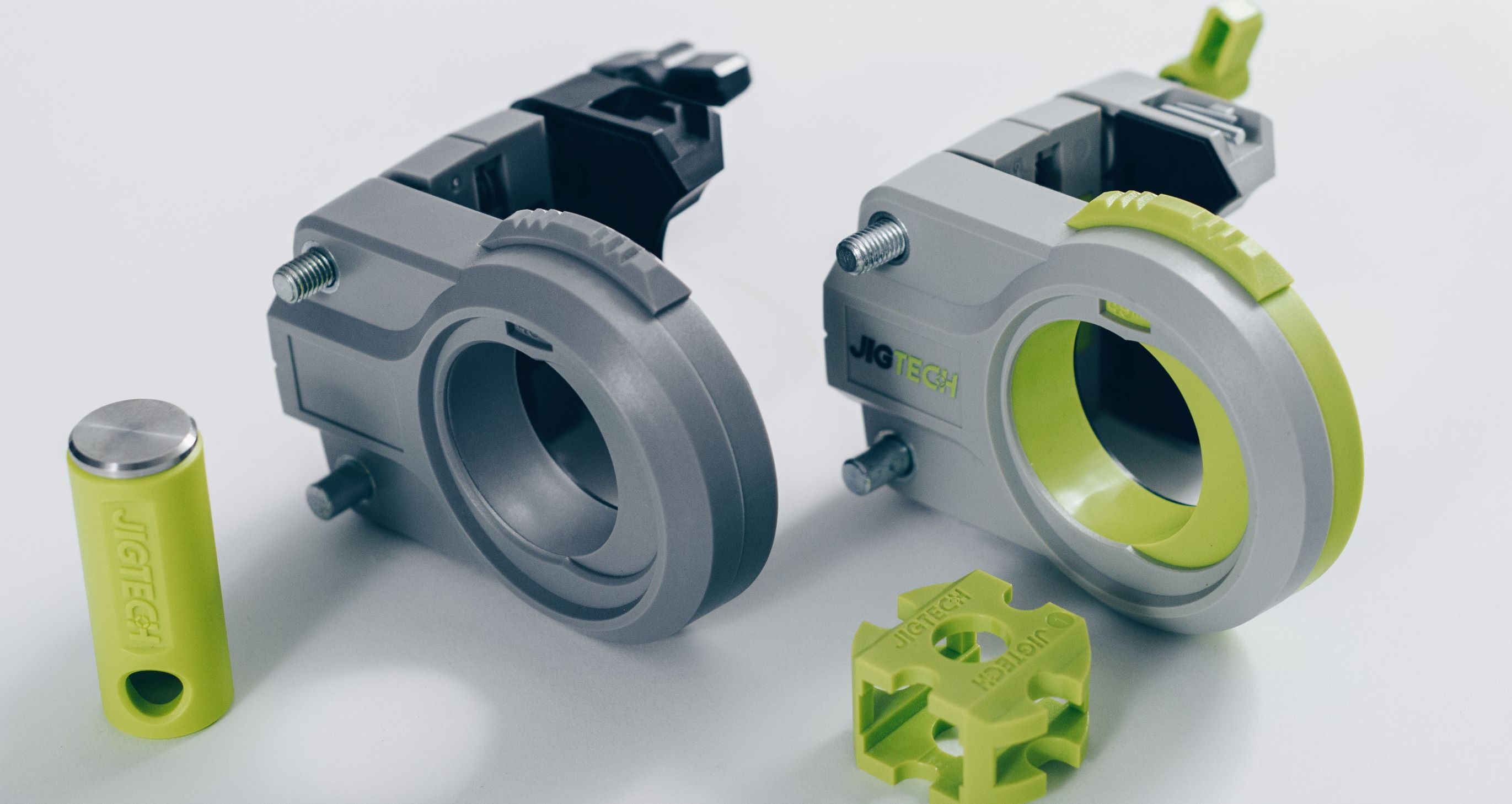
Bringing a new product to life is an exciting journey, but transitioning from a prototype to full-scale production is where many businesses face their biggest challenges. Scaling up requires careful planning, the right manufacturing partners, and an understanding of cost, quality control, and supply chain management. Here’s what you need to know to ensure a smooth transition.
1. Validate Your Prototype for Mass Production
Before jumping into production, ensure your prototype is optimised for manufacturability. Just because a prototype works doesn’t mean it can be easily or affordably mass-produced. Consider:
Design for Manufacturing (DFM): Adjusting your design to reduce complexity, minimise material waste, and ensure compatibility with mass production techniques.
Material Selection: The materials used in prototyping (e.g., SLA resin or other 3D-printed plastics) might not be suitable for full-scale manufacturing. Choose materials that balance cost, durability, and performance.
Testing & Refinement: Conduct stress tests, user trials, and compliance checks to ensure the product meets industry standards and customer expectations.
2. Choose the Right Manufacturing Process
Not all production methods are suitable for every product. Consider these options:
Injection Moulding: Ideal for high-volume plastic parts due to low per-unit cost once tooling is created.
CNC Machining: Great for precision components, especially in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. But can be costly.
3D Printing: Suitable for low to medium volume production, custom smaller parts, and complex geometries.
Vacuum casting & Reaction injection moulding: Best for larger, high-strength parts that require durability. Typically cheaper than traditional manufacturing methods for volume production.
Choosing the right process will depend on your production volume, budget, and material needs.
3. Find the Right Manufacturing Partner
Selecting a manufacturer is one of the most critical steps in scaling up. Look for:
Experience in Your Industry: A manufacturer familiar with your product type will help you avoid costly mistakes.
Scalability: Ensure they can handle increasing production volumes as demand grows.
Quality Control Measures: Check their certifications, quality assurance processes, and compliance with industry standards.
Communication & Reliability: A responsive and transparent manufacturer can save you from production delays and miscommunications.
4. Manage Costs & Production Efficiency
Scaling up requires a balance between cost and quality. Consider:
Tooling & Setup Costs: Injection moulding and other processes require upfront investment in moulds and tooling. Plan for these costs early.
Batch Production: Starting with small pre-production runs allows you to test the market before committing to high-volume manufacturing.
Supplier Negotiations: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved lead times, and more reliable deliveries.
5. Establish a Quality Control System
Mass production introduces new risks, such as defects and inconsistencies. A strong quality control process should include:
Pre-production Testing: Ensuring materials and components meet specifications.
In-Process Inspections: Checking for defects during production rather than waiting until the final stage.
Post-Production Quality Assurance: Conducting final inspections before shipment to ensure consistency.
6. Plan Your Supply Chain & Logistics
Efficient supply chain management ensures you can meet demand without delays. Key considerations include:
Sourcing Materials: Reliable suppliers for raw materials and components.
Inventory Management: Avoid overproduction or underproduction by analysing demand forecasts.
Shipping & Distribution: Whether using a third-party logistics (3PL) provider or managing distribution in-house, plan for storage, handling, and fulfilment.
7. Prepare for Scaling & Market Demand
Once production is running smoothly, be ready to scale further by:
Gathering Customer Feedback: Use early sales data and customer reviews to refine your product before mass distribution.
Automating Where Possible: Implementing automation in production can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Building a Support Network: Having contingency plans for supplier issues, design changes, or unexpected demand spikes.
Conclusion
Transitioning from prototype to full-scale production is a crucial step in bringing a new product to market. By optimising your design for manufacturability, selecting the right production process, ensuring quality control, and managing costs effectively, you can avoid common pitfalls and set your business up for long-term success.
Are you currently working on scaling up production for a new product? Need to ensure design for manufacturability? Contact our design team at design@ame-3d.co.uk.